Welcome to Nural's newsletter focusing on how AI is being used to tackle global grand challenges.
Packed inside we have
- Meta using AI to decode speech from brain activity for the speechless
- AI helps recreate Van Gogh's previously lost and concealed 'Two Wrestlers'
- and new AI guided fish harvesting is more humane and less wasteful
If you would like to support our continued work from £1 then click here!
Marcel Hedman
This weeks newsletter is brought to you by Wynter.

Wynter, a customer feedback tool, is looking for data science professionals (CEOs, senior leaders, MLEs, data scientists) to join its paid research panels.
Participate in messaging research panel surveys, get paid for your insights.
It takes ~1-15 min to be part of a single research panel. Super low time commitment.
Join Wynter’s Paid Data Science Panels | Learn More
Key Recent Developments
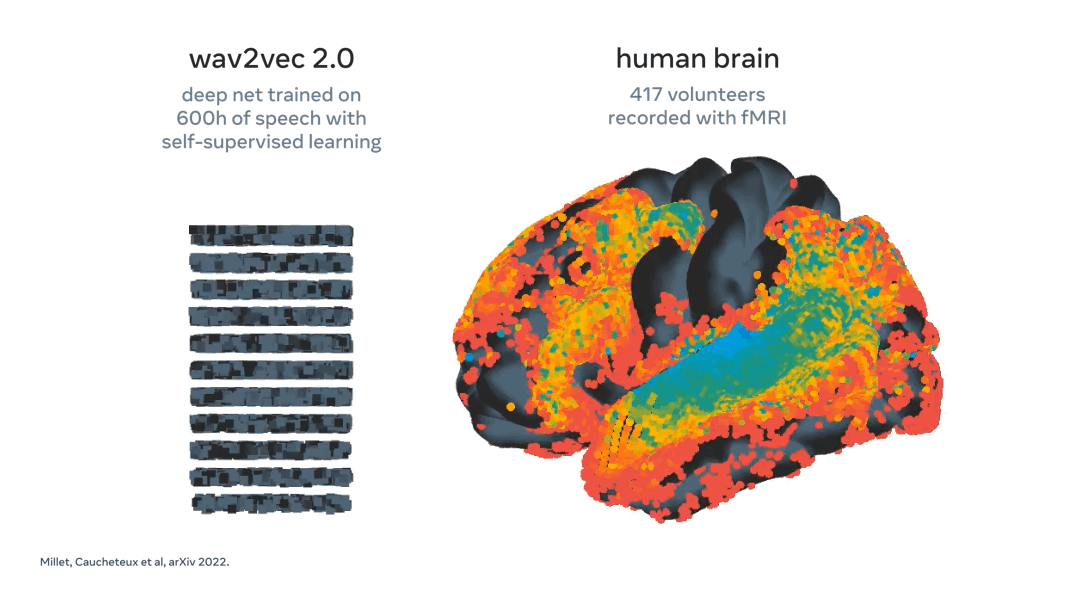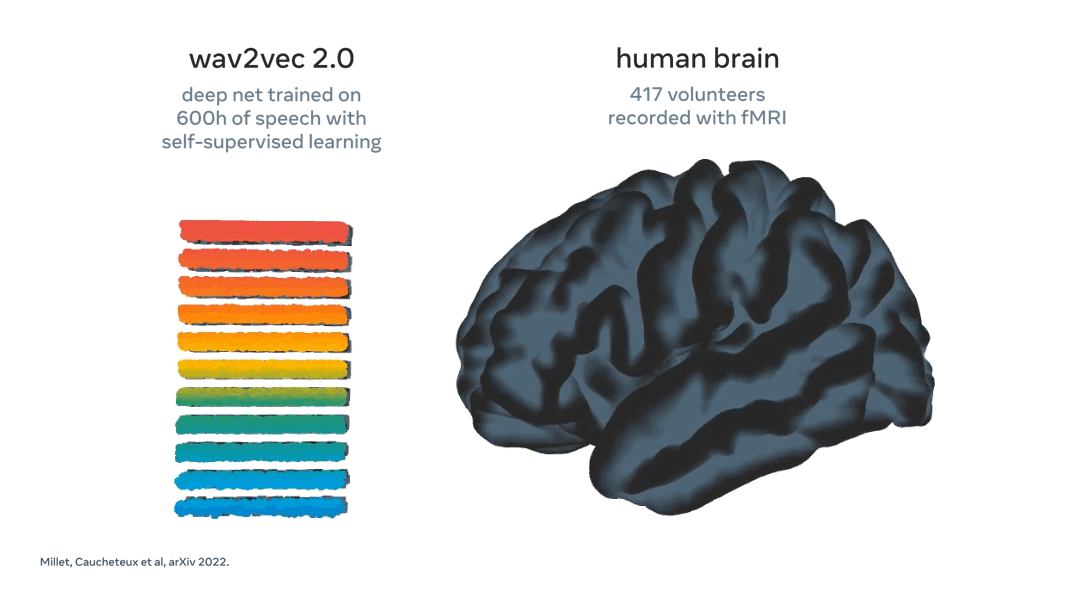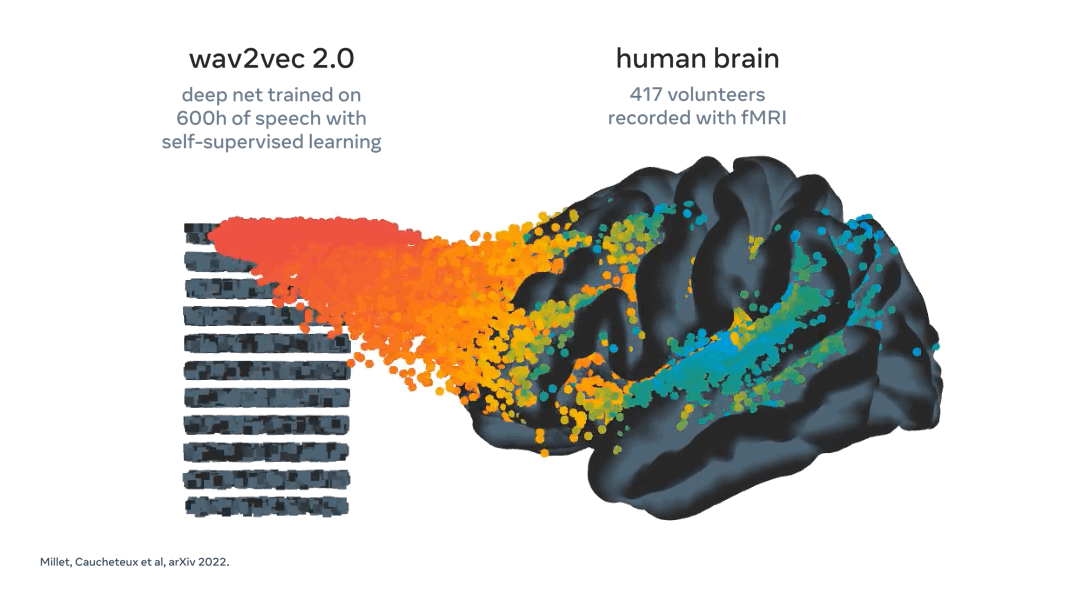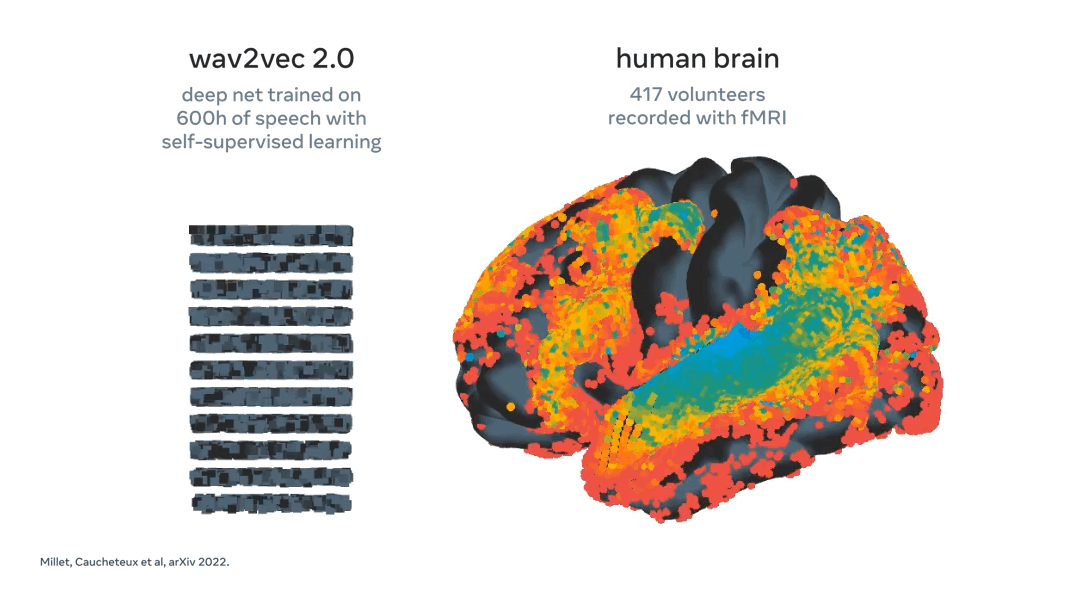
Meta using AI to decode speech from brain activity

What: Every year, more than 69 million people around the world suffer traumatic brain injury, which leaves many of them unable to communicate through speech, typing, or gestures. These people’s lives could dramatically improve if researchers developed a technology to decode language directly from non-invasive brain recordings.
In direct response to this challenge, Meta have developed a model that can "decode the corresponding speech segments with up to 73 percent top-10 accuracy from a vocabulary of 793 words, i.e., a large portion of the words we typically use on a day-to-day basis."
Key Takeaway: The ability to interact and communicate with those around you is a blessing often taking for granted. This work by Meta could prove pivotal in increasing quality of life for those suffering from speech impairments. Additionally, a non-invasive technique means the technology can more easily be integrated into daily life. A great example of AI for good.
Side thought: It would be interesting to see if there words said better by our brain waves than what our mouths would in fact say...
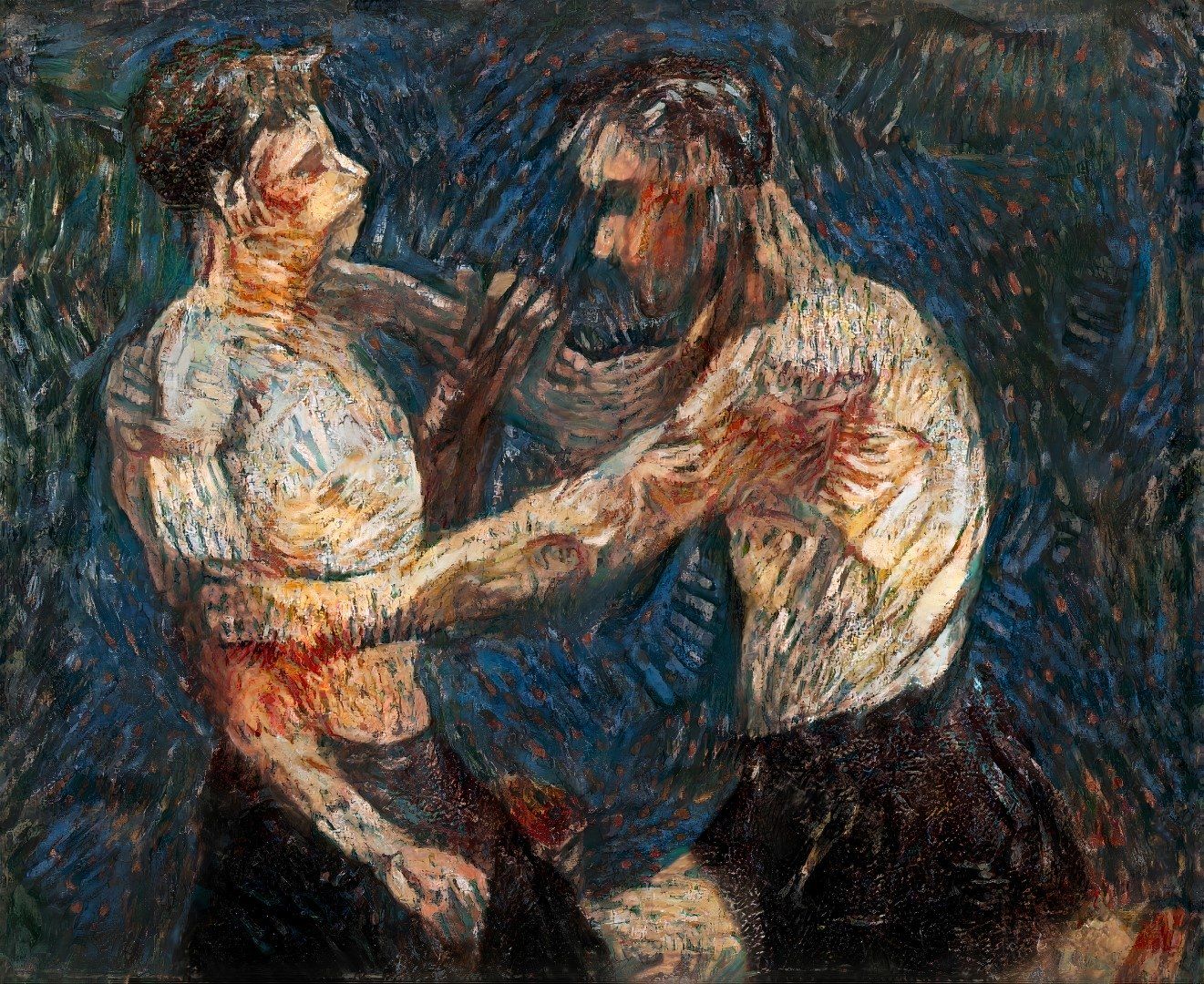
AI helps recreate Van Gogh's previously lost and concealed 'Two Wrestlers' painting
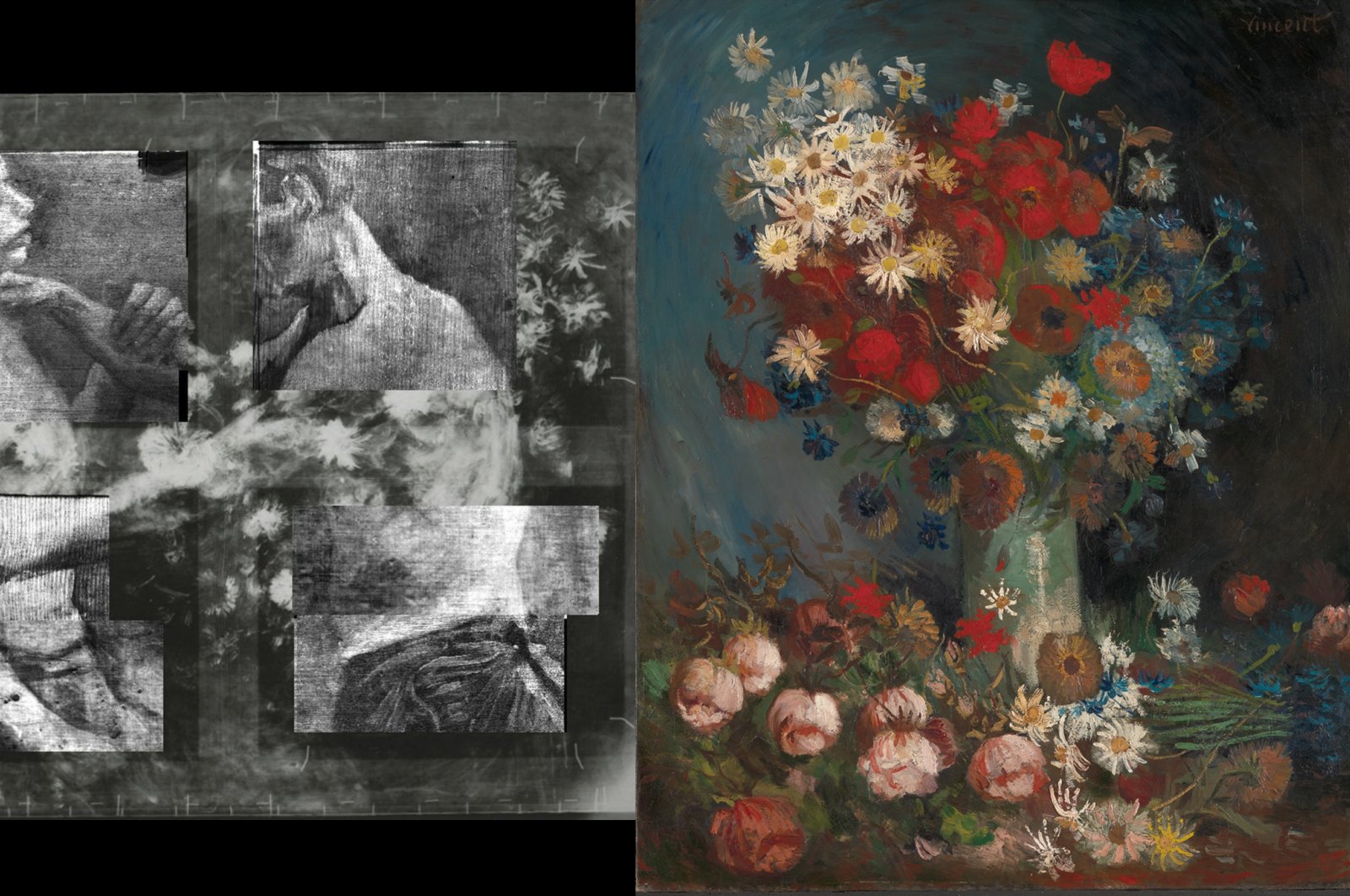

What: "A secret incomplete painting by Dutch artist Vincent Van Gogh has been recreated using artificial intelligence after 135 years after it was covered with a floral work titled "Still life with meadow flowers and roses."
The hidden incomplete painting was found using X-ray technology by British scientists in 2012 and the painting matches a description of the artwork described by a letter Van Gogh wrote to his brother. In the letter he wrote “This week I painted a large thing with two nude torsos – two wrestlers.”
Now, researchers at University College London have completed the artwork using a combination of AI, spectroscopy and 3D printing technology.
Key Takeaway: AI for good should also extend to art and creativity. Recently, there's been lots of focus on the ability of model's such as DALL-E to generate unique art, so it's very interesting to see these same techniques employed to finish the art of great artists of the past.

Shinkei Systems AI guided fish harvesting is more humane and less wasteful

What: Currently, the predominant method of catching and killing fish at scale includes using massive nets to catch fish and then bringing them all onboard a shift to suffocate over a period of minutes or hours.
This process is not only inhumane, but the stress released in the process produces chemicals, such as lactic acid, which causes the fish to degrade faster. This increase degradation rate eventually leads to wastage.
However, Shinkei Systems have found employed computer vision to automate what was once a traditional Japanese method. This method is more humane due to no prolonged suffering and also leads to less wastage as there's no build up of toxic chemicals in the fish's body.
Key Takeaway: One of the key benefits of AI is it's ability to rapidly automate tasks which are time consuming and complex. Sometimes combining bespoke knowledge from the past (traditional Japanese fishing) with technological advances of the future (computer vision + engineering) is what is required to build an optimal solution.
AI Ethics
🚀U.S. officials order Nvidia to halt sales of top AI chips to China
🚀 Predicting Alzheimer's using a multi-expert ML approach on clinical features [paper]
🚀 Google search will improve snippets to avoid misinformation
🚀 Seemingly ‘sentient’ AI needs a human in the loop [former co-head of Google’s AI Ethics unit]
🚀 DALL-E can now use AI to extend images as a human artist might
Other interesting reads
🚀 Launching an AI startup - From spycraft to startups [industry interview]
🚀 Rules of Machine Learning: Best Practices for ML Engineering
🚀 The next frontier for AI in China could add $600 billion to its economy [Mckinsey report]
🚀 Top Trending ML Papers of the Month [Twitter thread]
Cool companies found this week
Workplace safety
Protex - A Y Combinator-backed Irish company that aims to prevent workplace accidents before they happen. The company utilises artificial intelligence and computer vision to help identify unsafe behaviour in work settings and has secured $18M in seed and Series A round of funding.
Food wastage
Shinkei Systems - Computer vision guided automation of fish harvesting. Their technique is more humane and reduces wastage.
...and Finally
AI/ML must knows
Foundation Models - any model trained on broad data at scale that can be fine-tuned to a wide range of downstream tasks. Examples include BERT and GPT-3. (See also Transfer Learning)
Few shot learning - Supervised learning using only a small dataset to master the task.
Transfer Learning - Reusing parts or all of a model designed for one task on a new task with the aim of reducing training time and improving performance.
Generative adversarial network - Generative models that create new data instances that resemble your training data. They can be used to generate fake images.
Deep Learning - Deep learning is a form of machine learning based on artificial neural networks.
Best,
Marcel Hedman
Nural Research Founder
www.nural.cc
If this has been interesting, share it with a friend who will find it equally valuable. If you are not already a subscriber, then subscribe here.
If you are enjoying this content and would like to support the work financially then you can amend your plan here from £1/month!


